STEM education toolkit
Explore an approach to teaching and learning that incorporates co-creation, 21st-century learning, innovation and design thinking.
Grades 6 to 8 (Ontario)
Elementary cycle 3 to Secondary cycle 2 (Quebec)
Dig deep into inquiry- and problem-based learning with your students using the STEM education toolkit and the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. The outline below is intended for teachers delivering the Ontario curriculum to students in Grades 6 to 8; however, the toolkit can also be adapted for use with any grade level or province/territory.
Access the entire STEM education toolkit on Google Drive to view and download lesson plans, instructional slides, curriculum connections and worksheets.
Access the STEM education toolkit
Share :
How to use this toolkit
- Identify a topic of interest or relevance based on the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals in order to contextualize the problem-based design project for students.
- Prepare students for the design project by having them complete two or three skill challenges of your choice.
- Support students as they complete the design project by helping them:
- Connect to the curriculum
- Design innovative solutions
- Create and test prototypes
To support teachers and students through this learning experience, this toolkit includes:
- Lesson plans and instructional slides for the problem-based design project and skill challenges
- Student handouts and worksheet
- Sample student evaluation tools
- Hand tool safety resources
The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals
In 2015, the United Nations adopted 17 sustainable development goals with the aim of addressing and tackling 17 global issues by 2030. These goals represent a call-to-action for teachers, students and people of all ages to create a better future together. To learn more, visit the United Nations’ website.
To complete the problem-based design project, select one goal. Choose a goal based on curriculum connections and your students’ interests. For example, you could explore and improve your local community by focusing on goal 11: sustainable cities and communities.
View the curriculum connections for more detailed grade- and subject-specific connections.
Curriculum links to global goals
Various curricula are addressed through problem-based learning and design that are not captured in the outline below. Specific expectation connections from the science and technology, mathematics, and language curricula are detailed in the skill challenge lesson plans and the problem-based design project lesson plans. the connections listed below are best addressed through initial inquiry into the chosen global goal (problem-based design project, lesson 1).
The below global goals are taken from this guide to teaching the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals.
| Global goal | Curriculum connections by grade in Ontario |
|---|---|
No poverty
| Grade 6:
Social studies; People and environments: Canada’s interactions with the global community
Grade 8: Geography; Global inequalities: Economic development and quality of life |
Zero hunger
| Grade 6:
Social studies; People and environments: Canada’s interactions with the global community
Grade 7: Geography; Natural resources around the world: Use and sustainability Grade 8: Geography; Global inequalities: Economic development and quality of life |
Good health and well-being
| Grade 6, 7, 8:
Healthy living; Substance use, addictions, and related behaviours; Human development and sexual health; Mental health literacy
Grade 8: Geography; Global inequalities: Economic development and quality of life |
Sustainable cities and communities
| Grade 6:
Social studies; People and environments:
Canada’s interactions with the global
Community; Science and technology; Electricity and electrical devices
Grade 7: Geography; Natural resources around the world: Use and sustainability; Science and technology; Form and function Grade 8: Geography; Global settlement: Patterns and sustainability; Science and technology; Water systems |
Life below water
| Grade 6:
Science and technology; Biodiversity
Grade 7: Science and technology; Interaction in the environment Grade 8: Science and technology; Water systems |
Life on land
| Grade 6:
Science and technology; Biodiversity
Grade 7: Geography; Natural resources around the world: Use and sustainability; Science and technology; Interaction in the environment Grade 8: Geography; Global settlement: Patterns and sustainability |
Skill challenges
Support students’ skill development by selecting two or three skill challenges based on grade-specific curriculum connections, available materials and your students’ interests. Low-tech challenges are available and have been indicated below.
Note: Connections to the Grade 5 curriculum have been included to accommodate educators who teach split-grade classes.
Accessibility challenge (Low-tech)
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Form and function (7)
- Systems in action (8)
Target skills
- Micro:bit (optional)
- Circuit building (optional)
- Innovation and iteration
- Prototype sketching
Elastic racer
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Data management
- Conservation of energy and resources (5)
- Form and function (7)
Target skills
- Hand-tool use
Electric racer
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Data management
- Electricity and electrical devices (6)
- Form and function (7)
Target skills
- Hand-tool use
- Circuit building
Farm alarm
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Electricity and electrical devices (6)
- Systems in action (8)
Target skills
- Micro:bit
- Circuit building
- Innovation and iteration
- Prototype sketching
Identity cube (Low-tech)
Curriculum connections
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Visual arts
- Form and function (7)
Target skills
- Hand-tool use
- Spatial awareness
Laika 2.0 (Low-tech)
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Conservation of energy and resources (5)
- Flight (6)
- Space (6)
Target skills
- Use of loose parts
- Innovation and iteration
- Prototype sketching
Marble coasters
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Conservation of energy and resources (5)
- Form and function (7)
Target skills
- Use of loose parts
- Innovation and iteration
- Prototype sketching
Micro:bit adventure
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Language arts
- Electricity and electrical devices (6)
- Systems in action (8)
Target skills
- Micro:bit
- Circuit building
Milk carton sculptures (Low-tech)
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Form and function (7)
- Geometry and spatial sense (6 and 7)
Target skills
- Spatial awareness
Mousetrap racer
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Data management
- Systems in action (8)
Target skills
- Hand-tool use
Scribble bots
Curriculum connections
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Electricity and electrical devices (6)
Target skills
- Circuit building
- Innovation and iteration
Space lander (Low-tech)
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Data management
- Flight (6)
- Space (6)
- Form and function (7)
Target skills
- Use of loose parts
- Innovation and iteration
- Prototype sketching
Wind turbine (Low-tech)
Curriculum connections
- Technological problem-solving skills
- Scientific inquiry/experimentation skills
- Data management
- Conservation of energy and resources (5)
- Electricity and electrical devices (6)
- Form and function (7)
- Systems in action (8)
Target skills
- Hand-tool use
- Innovation and iteration
- Prototype sketching
Problem-based design project
Learn more about your chosen sustainable development goals through a problem-based design project. Using the lesson plans, guide students through the design of innovative solutions to problems relating to the selected sustainable development goal, and help them create prototypes to model the solutions they have designed.
Over the course of five lessons, students will:
- Lesson 1: Learn about the inquiry topic and select a focus for an innovation design.
- Lesson 2: Share prototype ideas with the class, receive feedback and make design improvements.
- Lesson 3: Improve design based on feedback, create a new sketch, list needed materials and produce a task list to divide the work.
- Lesson 4: Transform design sketch into a tangible prototype.
- Lesson 5: Share project by “selling” prototype idea to a panel of peer entrepreneurs.
Access the entire STEM education toolkit to view and download lesson plans, instructional slides, curriculum connections and worksheets.
The STEM Education Toolkit was developed in collaboration with the Ontario Science Centre. This project was made possible through the financial contribution of the Ontario Ministry of Education and the Government of Canada under the Canada–Ontario Agreement on Minority-Language Education and Second Official-Language Instruction, 2013-2014 to 2017-2018. Note that the content is binding only on its authors and does not necessarily reflect the views of the Ontario Ministry of Education or the Government of Canada.

You may also be interested in
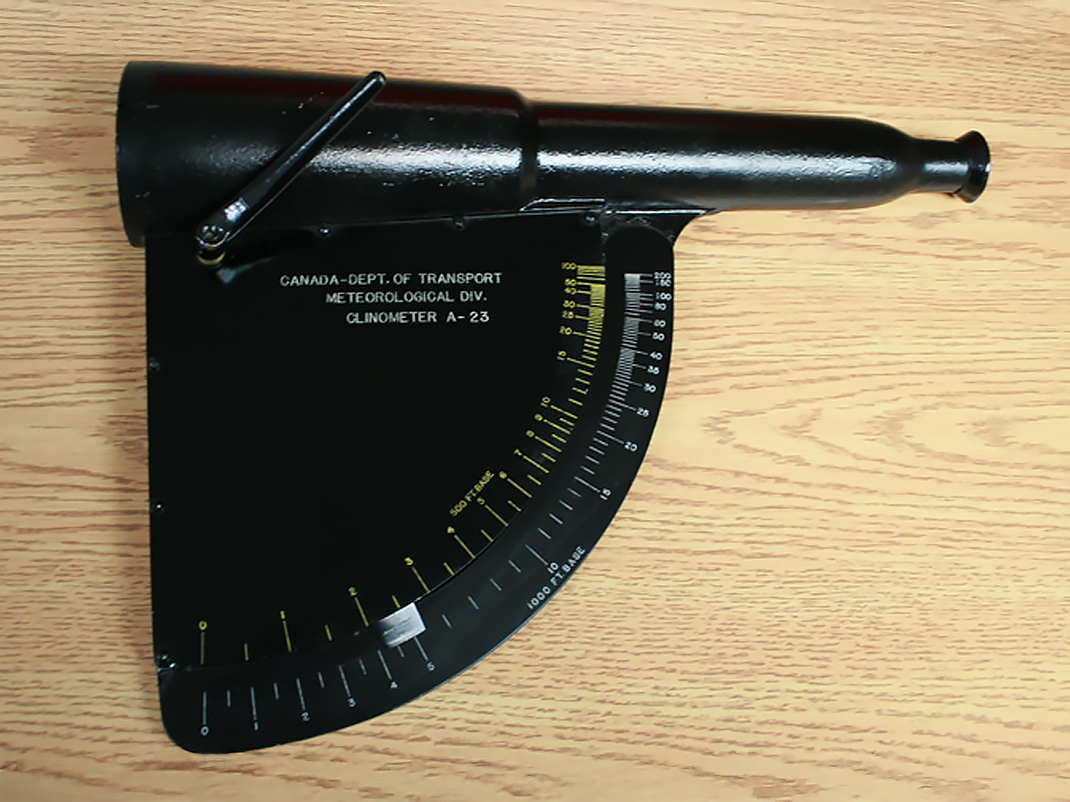

Clinometers
Find out how you can use a clinometer to determine how tall something is in your everyday life! Students can explore this 19th century tool through this educational resource from Ingenium, including downloadable 3D files and activity sheets.
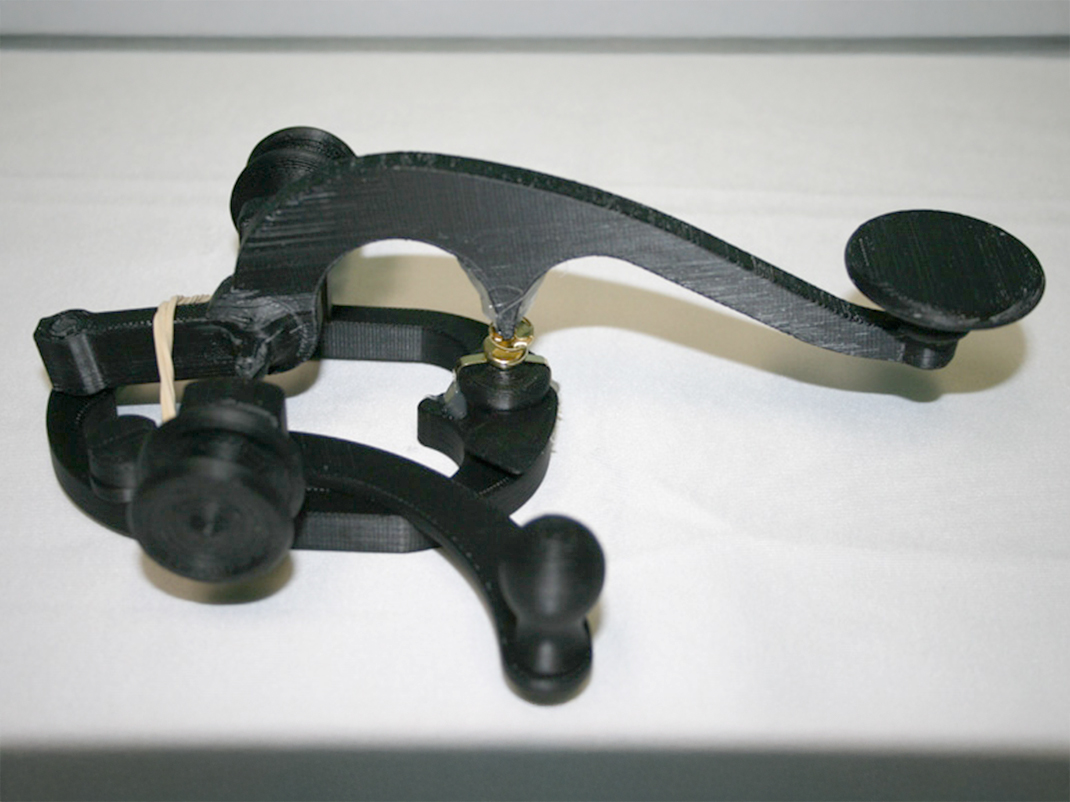

Telegraph key
Learn about the telegraph key, how it works and its importance in history using a 3D printed model and a series of fun, educational classroom activities. Put the telegraph key to work using Morse code and discover the importance of this revolutionary technology.
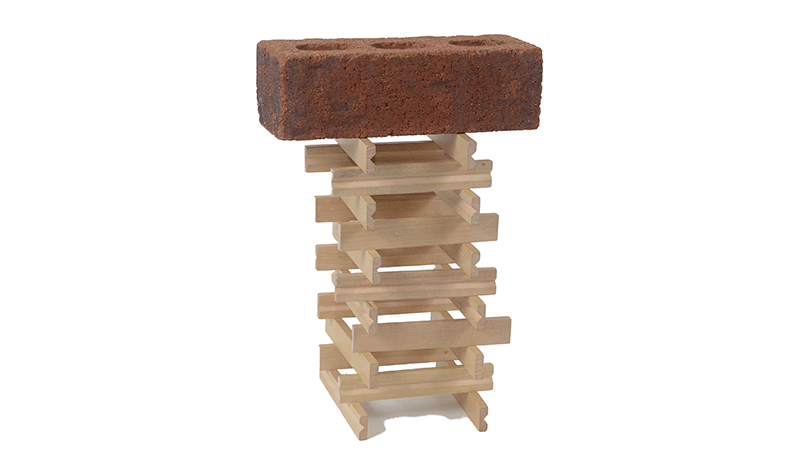

Stable structures
Through hands-on activities, students will become junior engineers as they explore the characteristics of strong and stable structures.