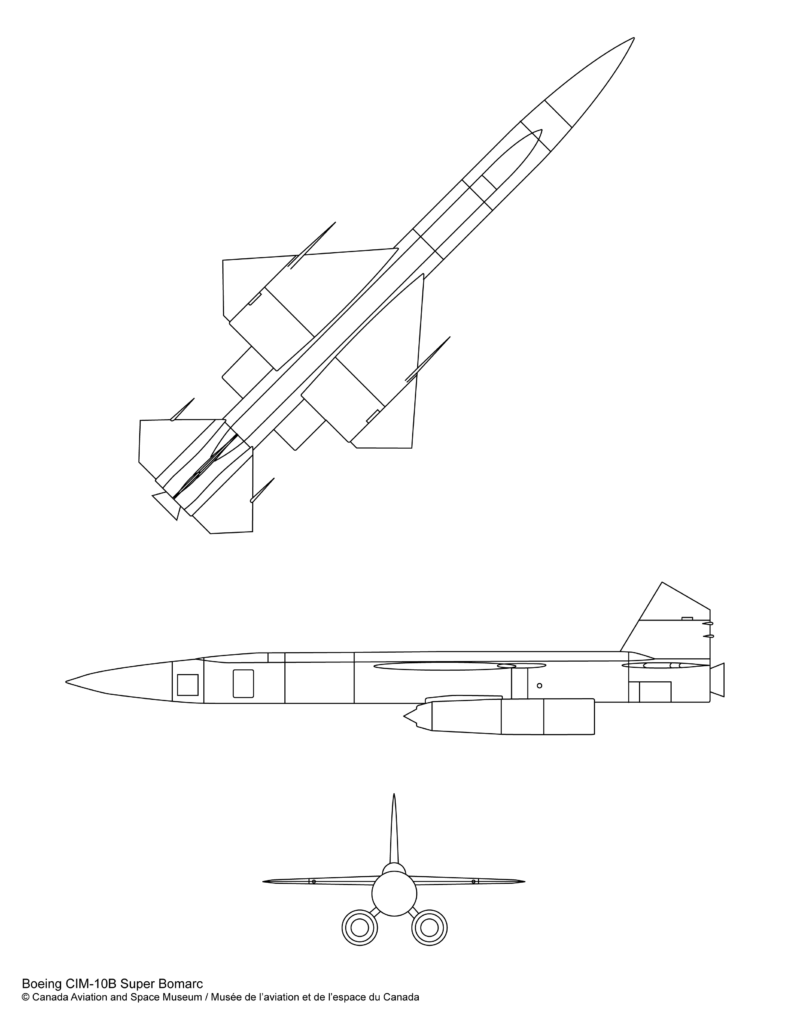
Boeing CIM-10B Super Bomarc
Highlights
- An American long-range, surface-to-air nuclear missile developed by Boeing Airplane Company (BO) and the Michigan Aeronautic Research Center (MARC) in 1950s; produced by Boeing from 1957 to 1964
- First long-range anti-aircraft missile in the world
- Operated by the U.S. Air Force and the RCAF until 1972 although never saw action
- Served with two RCAF missile squadrons as part of NORAD from 1962 to 1972
- Remotely launched by Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) computer control to intercept Soviet bombers
- Political debate surrounding Bomarc’s nuclear warheads played a significant role in the collapse of Canada’s minority government in 1963
- Once obsolete, Bomarcs served as target drones for testing more modern U.S. air-defence missiles
- First flight was in 1959 (MiM-10A)

Artifact no.: 1973.0009
Manufacturer: Boeing Airplane Company
Manufacturer location: United States
Manufacture date: 1960
Acquisition date: 1972
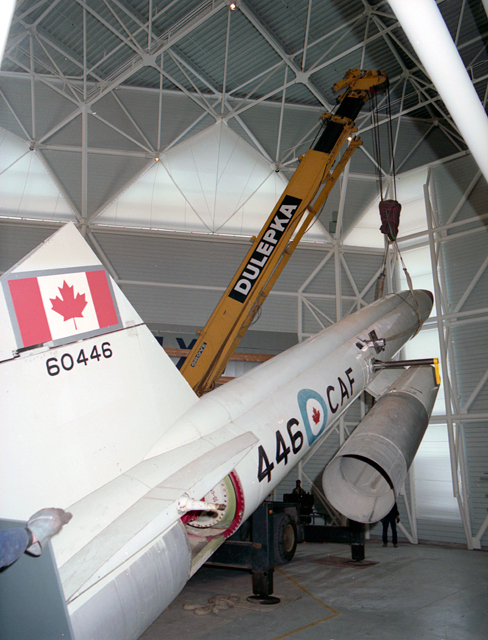
Registration number: 60446 (RCAF)
History
Introduced after the cancellation of the Avro Arrow, the Bomarc filled an anti-aircraft role as an unmanned long-range, surface-to-air weapon. By 1962 two RCAF Missile Squadrons were equipped with Bomarcs as part of the North American Air Defence Command (NORAD). Both squadrons formally disbanded on April 7, 1972. The Bomarcs were returned to the United States by September of that same year.
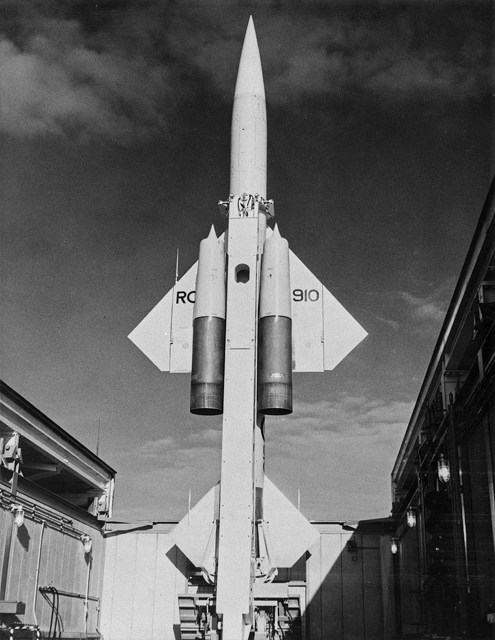
The Bomarc was a winged missile stored horizontally in a shelter from which it could be launched, after being raised vertically through a sliding roof. A solid-propellant booster rocket augmented the thrust of the two integral ramjet engines. Bomarc stands for Boeing Michigan Aeronautical Research Center.
Current location
The Cold War Exhibition, Canada Aviation and Space Museum
Provenance
Transfer from CAF
This Bomarc missile was manufactured by the Boeing Airplane Company in Seattle, Washington in July 1960. It was accepted by the RCAF and delivered to North Bay, Ontario, where it was in service with No. 446 Surface to Air Missile Squadron from 1962 until 1972, when it was withdrawn from Canadian service. The Canadian Armed Forces transferred the Bomarc to the Museum in July 1972.
Technical information
- Wing span
- 5.5 m (18 ft 2 in)
- Length
- 13.7 m (45 ft 1 in)
- Height
- 0.89 m (2 ft 11 in)
- Weight, empty
- Unknown
- Weight, gross
- 7,272 kg (16,032 lb)
- Cruising speed
- 3,434 km/h (2,134 mph)
- Max speed
- 3,434 km/h (2,134 mph)
- Rate of climb
- Unknown
- Service ceiling
- 30,480 m (100,000 ft)
- Range
- 700 km (440 mi)
- Power plant
- two Marquardt RJ43-MA-7, 5,440 kg (12,000 lb), thrust ramjets, plus one Thiokol XM-51 22,650 kg (50,000 lb) static thrust rocket engine